Analysis of cracking failure of sleeve coupling and improvement measures
My opinion:
The 4Cr5Mo2V drill bit sleeve(sleeve coupling) for hydraulic rock drill cracked after 10 days of use. The reasons for the cracking of the 4Cr5Mo2V drill bit sleeve were analyzed by fracture morphology observation, chemical composition analysis, mechanical properties and metallographic structure testing. The results show that the material and performance of the sleeve coupling meet the standard requirements, and the reason for the cracking of the drill bit sleeve is fatigue fracture caused by stress concentration at the surface laser engraving. A deformation layer appears at the end of the drill bit sleeve under the impact force, and the hardness increases due to work hardening, which is prone to cracking failure. It is recommended to use printed marking to avoid defects formed by laser engraving, reduce stress concentration on the surface of the drill bit sleeve, and increase the service life of the drill bit sleeve.

Introduction
The hydraulic rock drilling rig is an advanced rock drilling equipment used in mines, tunnels and underground projects using the drilling and blasting method. It realizes the mechanization and automation of drilling technology, frees construction workers from rock drilling work under harsh conditions and heavy labor, improves work efficiency and reduces pollution. The shank adapter sleeve is one of the important parts of the hydraulic rock drill buffer mechanism. The main function of the shank adapter sleeve is to play a limiting role between the shank adapter and the buffer piston. At the same time, it prolongs the life of the buffer piston under high-frequency impact. The shank adapter sleeve transfers the rebound energy to the buffer piston, and pushes the shank adapter to reset when the buffer piston returns. Due to the effect of cyclic impact force, the common failure form of the shank adapter sleeve is collapse.
The 4Cr5Mo2V shank adapter sleeve of a certain brand of rock drill is heated to 1010℃ in furnace-controlled atmosphere during processing, and tempered twice at 550℃ after oil quenching. The technical requirement is that the hardness is not less than 52HRC. The shank adapter sleeve cracked after 10 days of use. Different from the collapse failure mode of traditional shank adapter sleeves, the shank adapter sleeve cracked and collapsed at the end. By inspecting the macroscopic and microscopic morphology of the shank adapter sleeve fracture, the chemical composition, hardness, impact performance, inclusions and metallographic structure of the shank adapter sleeve, the cause of the cracking of the shank adapter sleeve is analyzed, which provides a theoretical basis for further improving the heat treatment process of the shank adapter sleeve and improving the life of the hydraulic rock drill.
1 Experimental process and results
1.1 Analysis of the macroscopic morphology of the drill bit sleeve
Figure 1 shows the side and end morphology of the failed drill bit sleeve for rock drill. It can be seen from the figure that the drill bit sleeve has an axially penetrating crack, which passes through the middle engraved line and extends along the arrow direction to the end of the drill bit sleeve; the other end of the crack is the root of the groove at the end of the drill bit sleeve. The sample was cut along the axis of the drill bit sleeve to observe the fracture morphology of the drill bit sleeve crack. At the same time, the material composition, hardness, impact absorption energy, inclusions and microstructure of the drill bit sleeve were tested and analyzed.
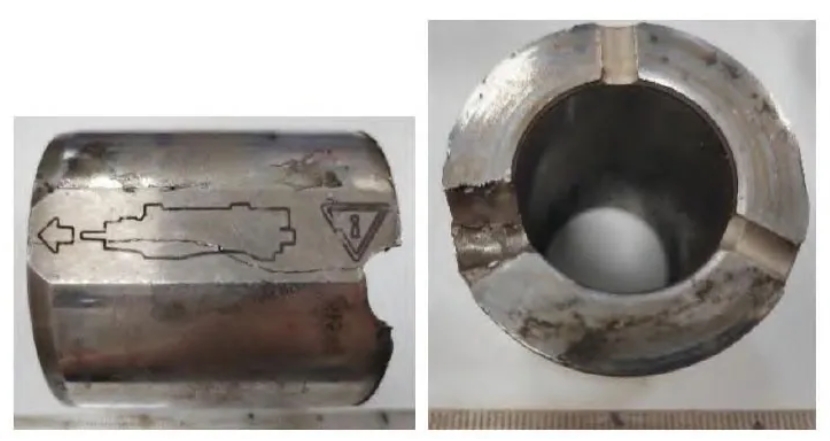

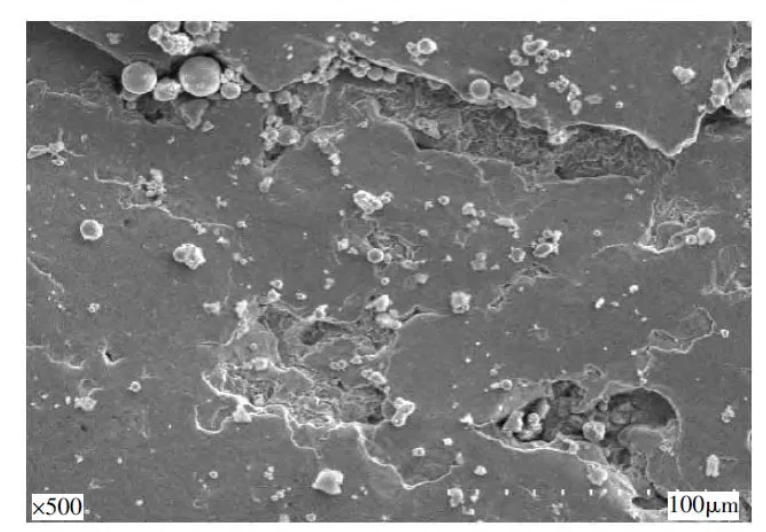
Figure 2 shows the macroscopic morphology of the drill bit sleeve fracture. It can be seen from the figure that the fracture is mainly divided into four areas: A, B, C and D. Area A is relatively flat and smooth, with arcs and radial lines inside. According to the direction of the arcs and radial lines, it can be seen that the elliptical area marked at 1 in Figure 2 is the crack source. Area B has large fluctuations, a relatively smooth surface, and arcs and radial lines inside. According to the direction of the arcs and radial lines, it can be inferred that area B originates from the elliptical area marked at 2 in Figure 2. Area C is relatively flat and smooth, with a large number of radial lines inside. According to the direction of the radial lines, it can be seen that area C originates from the left side of this area. Area D has large fluctuations, the left side is relatively smooth, and the right side is relatively rough. According to the morphological characteristics of area D, it can be seen that the left side of area D originates from area C on the left side of this area, and the right side originates from the surface of the shank adapter sleeve. According to the previous analysis, the crack of the shank adapter sleeve originates from the elliptical area 1 in Figure 2. Compared with the side morphology of the failed shank adapter sleeve in Figure 1, it can be seen that this place is the intersection of the left arrow line on the outer surface of the shank adapter sleeve.

1.2 Microscopic observation of fracture
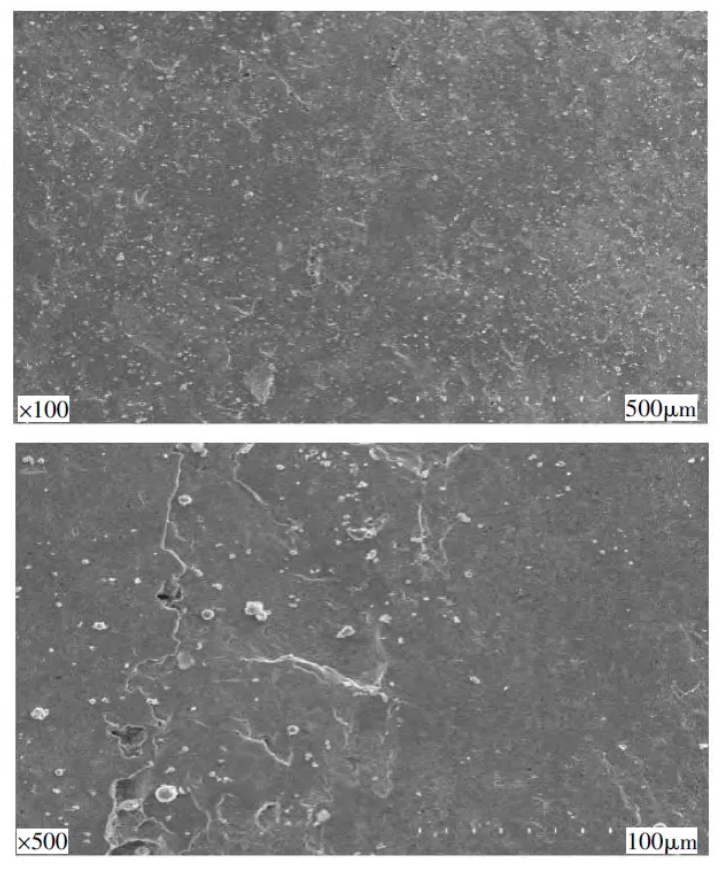
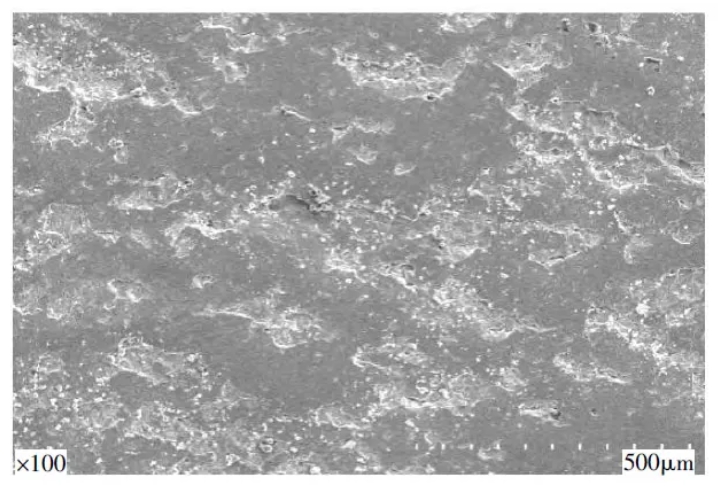
The various areas of the fracture in Figure 2 were observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Figure 3 is the low-power and high-power SEM images of the crack source area. It can be seen from the figure that the area is relatively flat in microscopic terms, and the surface has obvious plastic deformation, indicating that after the fracture is formed, it is squeezed against each other. Figure 4 shows low-power and high-power SEM images of the crack extension zone. It can be seen from the figure that its characteristics are similar to those of the crack source area. After the fracture is formed, plastic deformation occurs due to mutual extrusion. Compared with the two areas, the fracture plastic deformation is more serious due to the earlier formation of the crack source area, more fracture extrusion and friction times.
1.3 Chemical composition analysis of the shank adapter sleeve
The chemical composition of the shank adapter sleeve was tested using the spectrum. It can be seen that the shank adapter sleeve material meets the 4Cr5Mo2V steel composition requirements in the GB/T1299-2014 "Tool Steel" standard.
1.4 Mechanical properties test of the shank adapter sleeve
The samples were taken along the axis of the shank adapter sleeve, and the impact mechanical properties test was carried out according to the standard GB/T229-2020. The KU2 value of the shank adapter sleeve material is 28.7J.
1.5 Inclusions and metallographic structure analysis
The inclusions of the drill bit sleeve material were observed by optical microscope. According to the standard GB/T10561-2005 "Standard Rating Chart Microscopic Inspection Method for Determination of Non-metallic Inclusions in Steel", the non-metallic inclusions of the drill bit sleeve can be rated as A0, B0, C0, D0.5 and DS0.5.

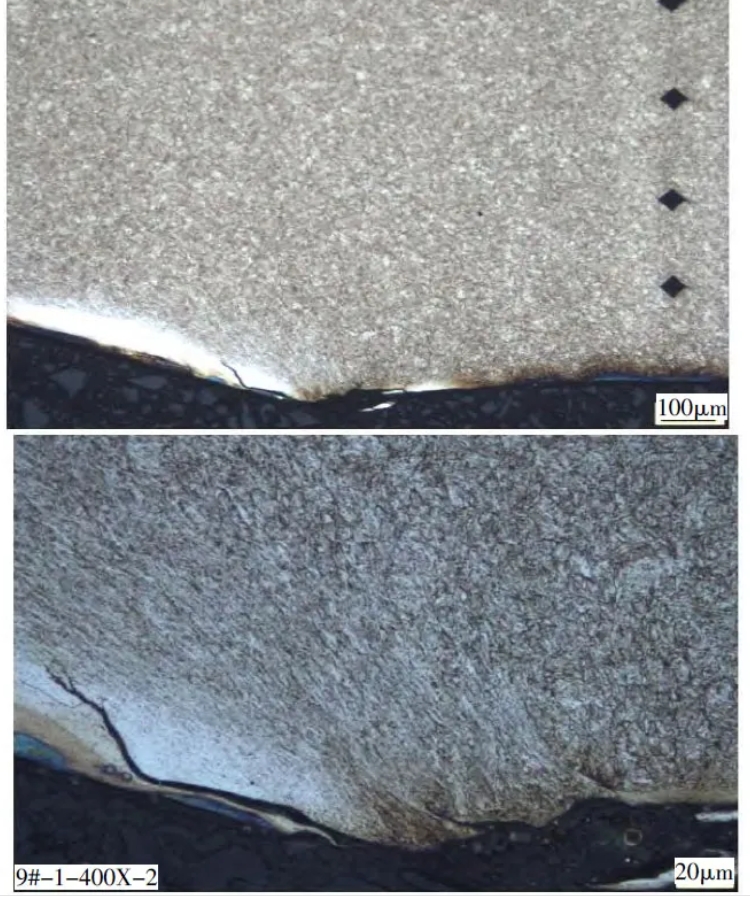
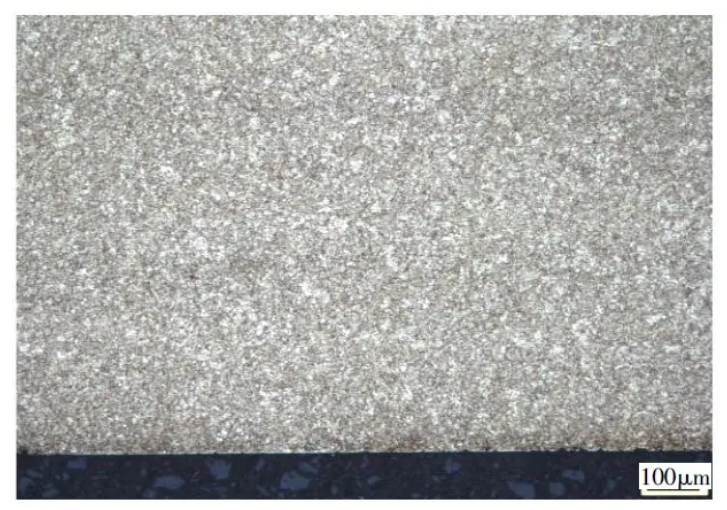
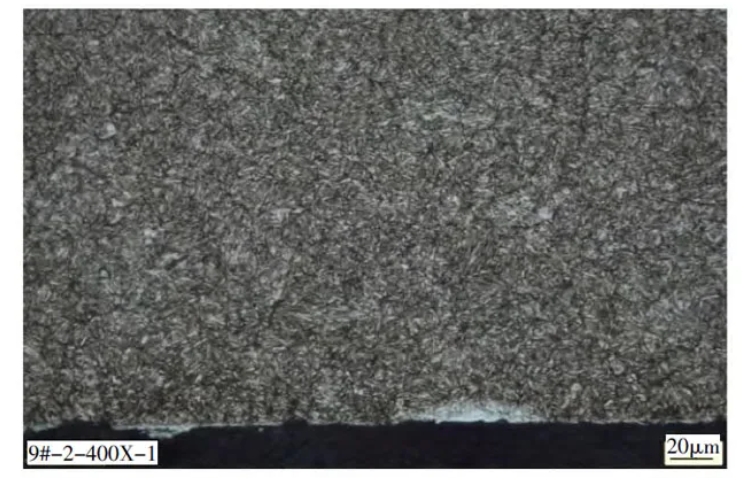
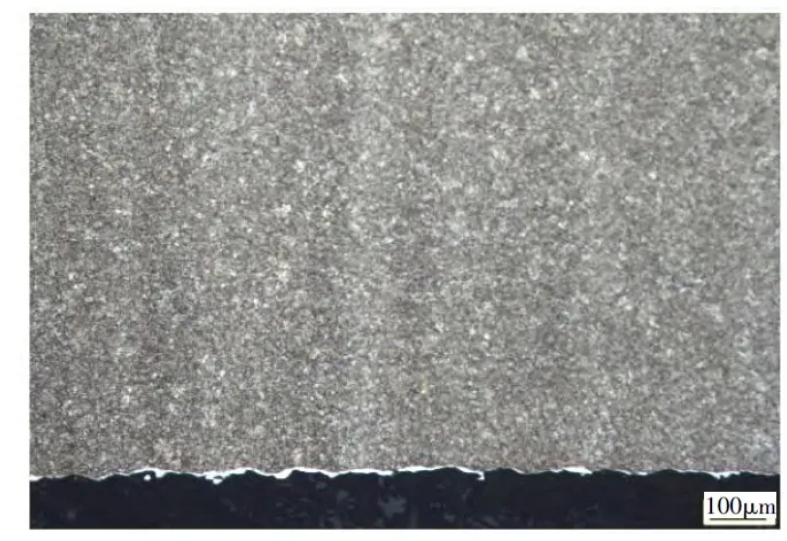
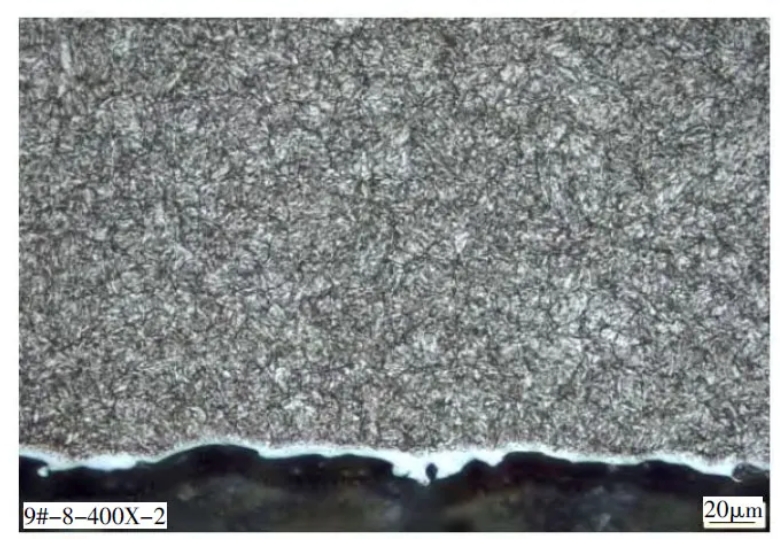
Figures 7 to 9 are microstructure diagrams of the end face, outer surface and core of the drill bit sleeve. It can be seen from the figure that the microstructure of each area of the drill bit sleeve is tempered troostite + carbide. There is a deformation layer formed by the interaction with the drill bit on the end face of the drill bit sleeve (white bright area in Figure 7). Due to the work hardening effect, the hardness of the end face of the drill bit sleeve is slightly higher. The white bright layer below the microstructure of the core of the drill bit sleeve is the oxide layer formed during the wire cutting process.




2 Result analysis
4Cr5Mo2V steel is based on the chemical composition of H13 steel. It is smelted by reducing the silicon content and increasing the V content. It has good hardenability, heat strength and wear resistance and is widely used in die casting molds, hot stamping molds and hot forging molds. The Mo element in the alloy improves the hardenability of the steel by improving the stability of supercooled austenite. At the same time, Mo is a strong carbide-forming element, which can improve the hardness, strength and wear resistance of the steel, increase the toughness and tempering stability of the steel. During the tempering process, the solid-dissolved vanadium precipitates in the form of V (C, N) compounds, which plays a precipitation strengthening and secondary hardening role, and enhances the high-temperature toughness and tempering stability of the steel. After annealing and quenching and tempering heat treatment, the hardness of the steel is not less than 52HRC, and the impact absorption energy reaches 28.7J. It has good surface wear resistance and core toughness. During use, the shank adapter sleeve can withstand cyclic impact and has a good fatigue life. Due to the need for installation and matching, the outer surface of the shank adapter sleeve is marked with laser lines. At the intersection of the arrow lines, there is stress concentration, forming a fatigue source, and the shank adapter sleeve produces fatigue fracture. The crack continues to expand under the impact force, forming a through crack in the shank adapter sleeve. Under the impact, the two end faces of the formed crack rub and squeeze each other, and the microscopic morphology of the fracture surface shows plastic deformation. Due to the impact force of the shank adapter and the buffer piston, a deformation layer appears at the end of the shank adapter sleeve. Due to the work hardening effect, the hardness of the end of the shank adapter sleeve increases, and it is easy to crack during long-term use.
According to the working environment and failure form of the shank adapter sleeve, it is recommended that the shank adapter sleeve marking adopts the printing mode to avoid damage to the surface of the shank adapter sleeve caused by the line marking, resulting in stress concentration and fatigue cracks in the shank adapter sleeve.
3 Conclusion
Through the inspection and analysis of the macroscopic and microscopic morphology of the shank adapter sleeve fracture, the chemical composition of the material, the hardness, the impact performance, the inclusions and the metallographic structure, it is found that the main reason for the cracking of the shank adapter sleeve is the fatigue fracture caused by the stress concentration at the surface laser line. The end of the shank adapter sleeve will have a deformation layer under the impact force, and the hardness of the end will increase due to work hardening, which will easily cause cracking and failure during use. It is recommended to use printed markings and defects formed by laser marking to reduce stress concentration on the surface of the shank adapter sleeve and increase the service life of the shank adapter sleeve.




